Lesson Planning is a stage in the formal educational process and that begins with
- Conducting a needs assessment
- Development of goals and objectives
- Conducting an occupational analysis DACUM
- Developing Units of instruction and course outlines
- Developing lessons
- providing instruction
- assessment and refining course.
The essential components of a lesson plan are time, resources and order of presentation
There are many guidelines and resources for lesson planning. Often the type of lesson plan that is used depends on the philosphy and approach to teaching. The approach to lesson planning is also also dependant on the subject matter and setting. Courses that are presenting strictly cognitive material and are organized around a 50 minute time slot require different planning than a lesson that involves a psychomotor skill with a lab or shop component. The latter require considerably more planning in terms of time and resources. As most guides to lesson planning point out, there is seldom strict adherence to a lesson plan as experienced teachers make adjustments and shift strategies on the fly.
Lesson planning depends upon earlier events in the planning cycle particularly developing course outlines and units of instruction.
Blooms
taxonomy provides a useful frame work for planning by dividing learning tasks into cognitive, affective and psychomotor domains.
A further taxonomy allows for a distinction between the level of accomplishment expected as a consequence of instuction general knowledge, working knowledge and qualified knowledge.
A course outline should specify the dominant domain and the expected level of knowlege.
Once these things have been determined a plan can be developed to deliver instruction that will meet this goal. As long as the outline is realistic in terms of expectations given time and resources the lesson plan can be fairly mechanical often completed in a
template. So a lesson is being planned to teach the boline knot.
What domain?
What level of learning?
How much time is required?
What resources are necessary?
How will we know when the lesson is learned?
Gagnes 9 Units of Instruction provides a guide for understaning the tasks that should be considered when devising a lesson plan .
1) gaining attention (reception)
(2) informing learners of the objective (expectancy)
(3) stimulating recall of prior learning (retrieval)
(4) presenting the stimulus (selective perception)
(5) providing learning guidance (semantic encoding)
(6) eliciting performance (responding)
(7) providing feedback (reinforcement)
(8) assessing performance (retrieval)
(9) enhancing retention and transfer (generalization).
Employability skills are mostly tasks that involve the affective domain.
DESCASome the characteristics of successful teachers
flexibility
sensitivity
and as
Dr. Andy Chun describes, agility
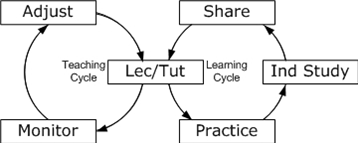
The Teaching Cycle (on the left of the diagram) is for teachers on the right is for the learner.
Another important characteristic is the ability to reflect and modify instruction based on feed back from a variety of sources.
An article on the
reflective teacher.
Feed back is essential to lesson planning and one of the main issues is "Are they learning what Iam trying to teach."
I know learning is occuring
when ......

